Connexion à WIS2 via MQTT
Objectifs d'apprentissage
À la fin de cette session pratique, vous serez capable de :
- vous connecter au Global Broker de WIS2 en utilisant MQTT Explorer
- examiner la structure des topics WIS2
- examiner la structure des messages de notification WIS2
Introduction
WIS2 utilise le protocole MQTT pour annoncer la disponibilité des données météorologiques, climatiques et hydrologiques. Le Global Broker de WIS2 s'abonne à tous les WIS2 Nodes du réseau et republie les messages qu'il reçoit. Le Global Cache s'abonne au Global Broker, télécharge les données contenues dans le message, puis republie le message sur le topic cache avec une nouvelle URL. Le Global Discovery Catalogue publie les métadonnées de découverte provenant du Broker et fournit une API de recherche.
Voici un exemple de structure de message de notification WIS2 pour un message reçu sur le topic origin/a/wis2/br-inmet/data/core/weather/surface-based-observations/synop :
{
"id":"3c14d7bf-e6b9-4f59-b4ea-f2fc52a33cd3",
"type":"Feature",
"conformsTo":[
"http://wis.wmo.int/spec/wnm/1/conf/core"
],
"geometry":{
"coordinates":[
-99.1964,
19.404,
2314
],
"type":"Point"
},
"properties":{
"data_id":"br-inmet:data:core:weather:surface-based-observations:synop/WIGOS_0-20000-0-76679_20250206T231600",
"datetime":"2025-02-06T23:16:00Z",
"pubtime":"2026-01-20T13:14:52Z",
"integrity":{
"method":"sha512",
"value":"qtlI3Noay2I4zcdA1XCpn8vzVLIt0RKrR398VGFgTttc1XRUVb4dHWNCDKPXUo4mNkiFKx5TTHBvrxlzqWmMnQ=="
},
"metadata_id":"urn:wmo:md:br-inmet:data:core:weather:surface-based-observations:synop",
"wigos_station_identifier":"0-20000-0-76679"
},
"links":[
{
"rel":"canonical",
"type":"application/bufr",
"href":"http://localhost/data/2025-02-06/wis/urn:wmo:md:br-inmet:data:core:weather:surface-based-observations:synop/WIGOS_0-20000-0-76679_20250206T231600.bufr4",
"length":125117
},
{
"rel":"via",
"type":"text/html",
"href":"https://oscar.wmo.int/surface/#/search/station/stationReportDetails/0-20000-0-76679"
}
],
"generated_by":"wis2box 1.2.0"
}
Dans cette session pratique, vous apprendrez à utiliser l'outil MQTT Explorer pour configurer une connexion client MQTT à un Global Broker WIS2 et afficher les messages de notification WIS2.
MQTT Explorer est un outil utile pour parcourir et examiner la structure des topics d'un broker MQTT donné afin de consulter les données publiées.
À propos de MQTT
MQTT Explorer fournit une interface conviviale pour se connecter à un broker MQTT et explorer les topics et la structure des messages utilisés par WIS2.
En pratique, MQTT est conçu pour la communication machine-à-machine, où une application ou un service s'abonne à des topics et traite les messages de manière programmatique en temps réel.
Pour travailler avec MQTT de manière programmatique (par exemple, en Python), vous pouvez utiliser des bibliothèques client MQTT telles que paho-mqtt pour vous connecter à un broker MQTT et traiter les messages entrants. Il existe de nombreux logiciels client et serveur MQTT, en fonction de vos besoins et de votre environnement technique.
Utilisation de MQTT Explorer pour se connecter au Global Broker
Pour afficher les messages publiés par un Global Broker WIS2, vous pouvez utiliser "MQTT Explorer", qui peut être téléchargé depuis le site web de MQTT Explorer.
Ouvrez MQTT Explorer et ajoutez une nouvelle connexion au Global Broker hébergé par MeteoFrance en utilisant les détails suivants :
- host : globalbroker.meteo.fr
- port : 8883
- username : everyone
- password : everyone
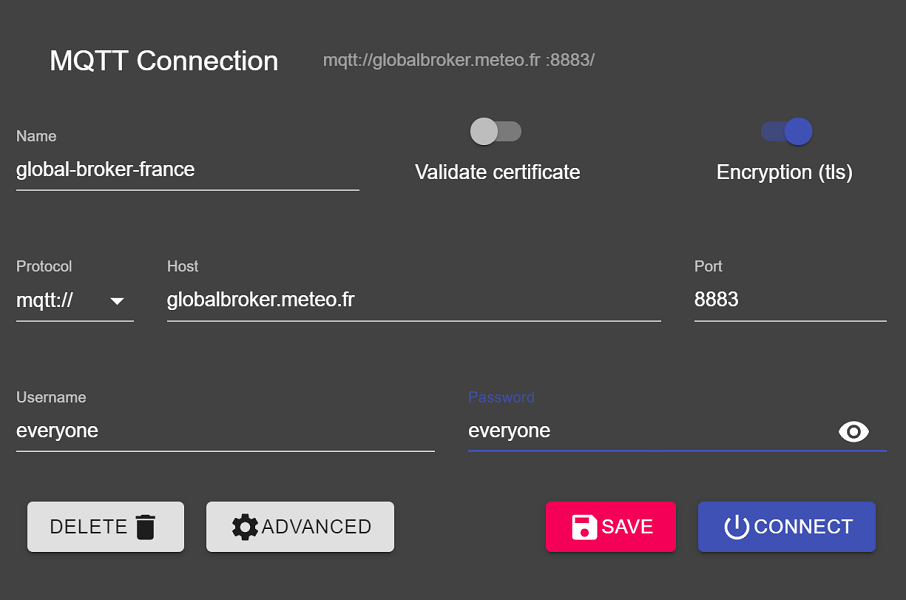
Cliquez sur le bouton 'ADVANCED', supprimez les topics préconfigurés et ajoutez les topics suivants pour vous y abonner :
origin/a/wis2/#
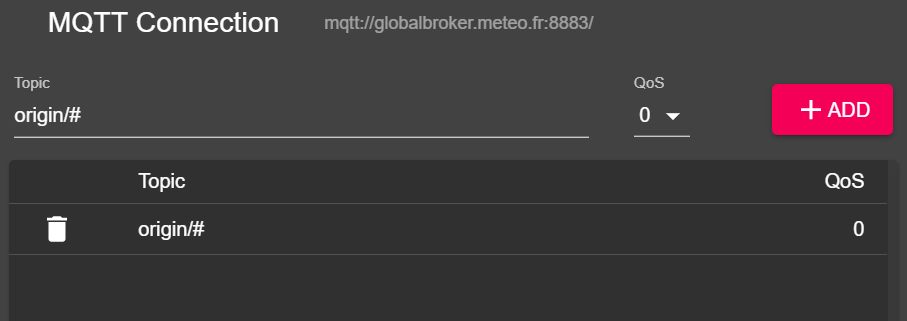
Note
Lors de la configuration des abonnements MQTT, vous pouvez utiliser les jokers suivants :
- Single-level (+) : un joker à un seul niveau remplace un seul niveau de topic
- Multi-level (#) : un joker à plusieurs niveaux remplace plusieurs niveaux de topics
Dans ce cas, origin/a/wis2/# s'abonnera à tous les topics sous le topic origin/a/wis2.
Cliquez sur 'BACK', puis 'SAVE' pour enregistrer vos détails de connexion et d'abonnement. Ensuite, cliquez sur 'CONNECT' :
Les messages devraient commencer à apparaître dans votre session MQTT Explorer comme suit :
Vous êtes maintenant prêt à explorer les topics et la structure des messages WIS2.
Exercice 1 : Examiner la structure des topics WIS2
Utilisez MQTT pour parcourir la structure des topics sous les topics origin.
Question
Comment pouvons-nous distinguer le centre WIS qui a publié les données ?
Cliquez pour révéler la réponse
Vous pouvez cliquer sur la fenêtre de gauche dans MQTT Explorer pour développer la structure des topics.
Nous pouvons distinguer le centre WIS qui a publié les données en regardant le quatrième niveau de la structure des topics. Par exemple, le topic suivant :
origin/a/wis2/br-inmet/data/core/weather/surface-based-observations/synop
nous indique que les données ont été publiées par un centre WIS avec l'identifiant br-inmet, qui correspond à l'Instituto Nacional de Meteorologia - INMET, Brésil.
Question
Comment pouvons-nous distinguer les messages publiés par les centres WIS hébergeant une passerelle GTS-to-WIS2 de ceux publiés par les centres WIS hébergeant un WIS2 Node ?
Cliquez pour révéler la réponse
Nous pouvons distinguer les messages provenant d'une passerelle GTS-to-WIS2 en regardant l'identifiant du centre dans la structure des topics. Par exemple, le topic suivant :
origin/a/wis2/de-dwd-gts-to-wis2/data/core/I/S/A/I/01/sbbr
nous indique que les données ont été publiées par la passerelle GTS-to-WIS2 hébergée par Deutscher Wetterdienst (DWD), Allemagne. La passerelle GTS-to-WIS2 est un type spécial de producteur de données qui publie des données du Global Telecommunication System (GTS) vers WIS2. La structure des topics est composée des en-têtes TTAAii CCCC pour les messages GTS.
Exercice 2 : Examiner la structure des messages WIS2
Déconnectez-vous de MQTT Explorer et mettez à jour les sections 'Advanced' pour modifier l'abonnement avec les topics suivants :
origin/a/wis2/+/data/core/weather/surface-based-observations/synopcache/a/wis2/+/data/core/weather/surface-based-observations/synop
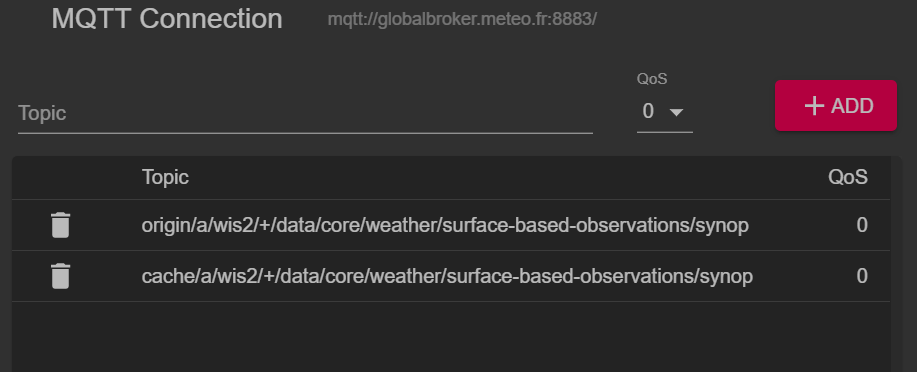
Note
Le joker + est utilisé pour s'abonner à tous les centres WIS.
Reconnectez-vous au Global Broker et attendez que les messages apparaissent.
Vous pouvez consulter le contenu du message WIS2 dans la section "Value" sur le côté droit. Essayez de développer la structure des topics pour voir les différents niveaux du message jusqu'à atteindre le dernier niveau et examinez le contenu d'un des messages.
Question
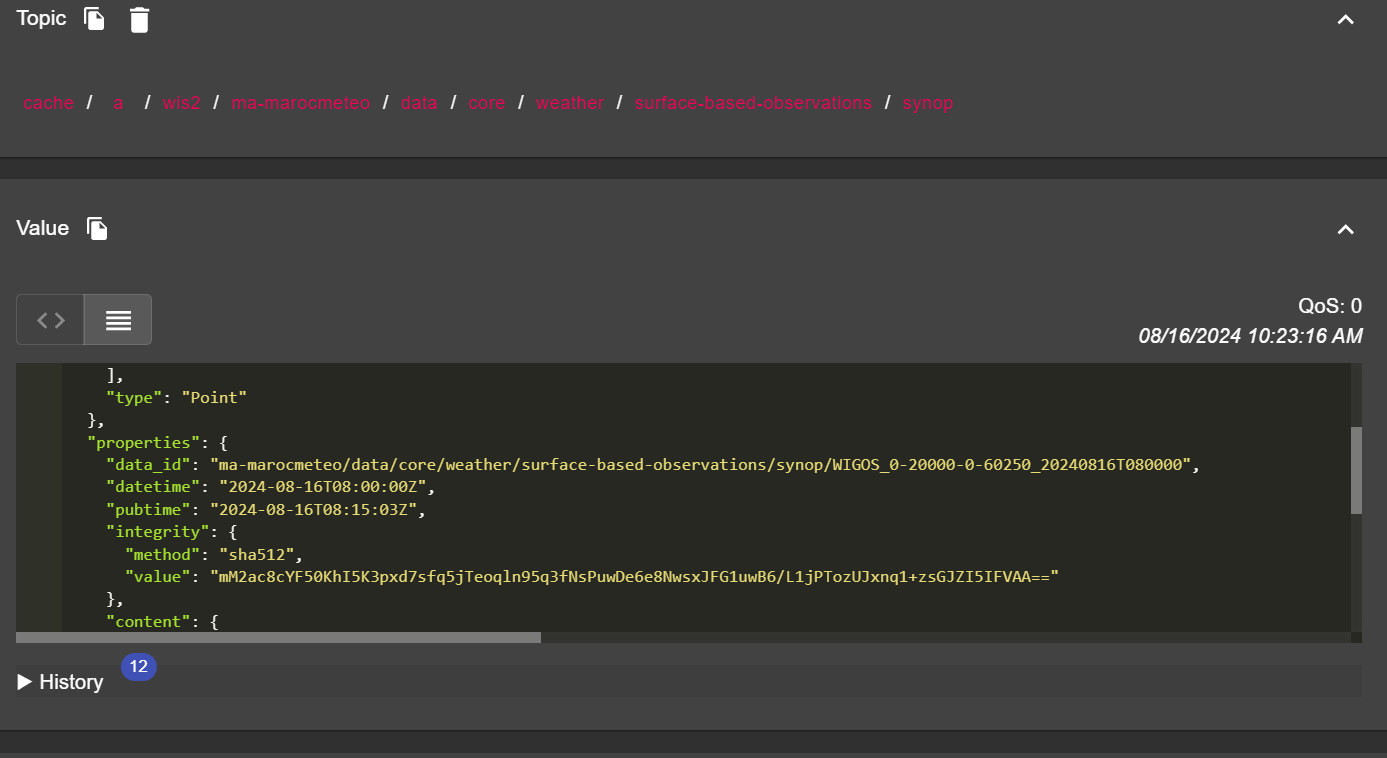
Comment pouvons-nous identifier l'horodatage de publication des données ? Et comment pouvons-nous identifier l'horodatage de collecte des données ?
Cliquez pour révéler la réponse
L'horodatage de publication des données est contenu dans la section properties du message avec une clé pubtime.
L'horodatage de collecte des données est contenu dans la section properties du message avec une clé datetime.
Question
Comment pouvons-nous télécharger les données depuis l'URL fournie dans le message ?
Cliquez pour révéler la réponse
L'URL est contenue dans la section links avec rel="canonical" et définie par la clé href.
Vous pouvez copier l'URL et la coller dans un navigateur web pour télécharger les données.
Exercice 3 : Examiner la différence entre les topics 'origin' et 'cache'
Assurez-vous d'être toujours connecté au Global Broker en utilisant les abonnements aux topics origin/a/wis2/+/data/core/weather/surface-based-observations/synop et cache/a/wis2/+/data/core/weather/surface-based-observations/synop comme décrit dans l'Exercice 2.
Essayez d'identifier un message pour le même identifiant de centre publié à la fois sur les topics origin et cache.
Question
Quelle est la différence entre les messages publiés sur les topics origin et cache ?
Cliquez pour révéler la réponse
Les messages publiés sur les topics origin sont les messages originaux que le Global Broker republie depuis les WIS2 Nodes du réseau.
Les messages publiés sur les topics cache sont les messages pour lesquels les données ont été téléchargées par le Global Cache. Si vous vérifiez le contenu du message provenant d'un topic commençant par cache, vous verrez que le lien 'canonical' a été mis à jour avec une nouvelle URL.
Il existe plusieurs Global Caches dans le réseau WIS2, vous recevrez donc un message de chaque Global Cache ayant téléchargé le message.
Le Global Cache ne télécharge et ne republie que les messages publiés dans la hiérarchie de topics ../data/core/....
Conclusion
Félicitations !
Dans cette session pratique, vous avez appris :
- comment s'abonner aux services du Global Broker WIS2 en utilisant MQTT Explorer
- la structure des topics WIS2
- la structure des messages de notification WIS2
- la différence entre les données core et recommandées
- la structure des topics utilisée par la passerelle GTS-to-WIS2
- la différence entre les messages du Global Broker publiés sur les topics
originetcache